How can the connection structure design of the trailer chain ensure its robustness and reliability?
Release Time : 2025-11-19
The design of a trailer chain's connection structure requires a multi-dimensional approach, encompassing material selection, structural optimization, process control, and auxiliary devices, to ensure its robustness and reliability under complex operating conditions. As a core component of the traction system, the trailer chain's connection structure must withstand dynamic loads, vibration, impact, and environmental corrosion; its design rationality directly affects the safety of the traction process.
Material selection is fundamental to the reliability of the connection structure. High-quality trailer chains typically utilize high-strength alloy steel or engineering plastics, such as quenched steel plates, chrome-plated chain plates, or nylon composite materials. These materials must possess high tensile strength, good toughness, and fatigue resistance to withstand the tensile, bending, and impact forces during traction. For example, steel drag chains undergo quenching to increase the hardness of the chain plates, and chrome plating enhances surface wear resistance, while plastic drag chains incorporate glass fiber or carbon fiber to strengthen their structural strength and prevent breakage.
Structural optimization is key to improving connection stability. A trailer chain's unit link typically consists of left and right chain plates and upper and lower cover plates, secured using embedded snap-fit or bolt designs. Embedded buckles are precision-molded to ensure a tight fit between chain links, preventing loosening. Bolted fasteners use high-strength bolts and nuts to increase preload at the connection points, preventing detachment due to vibration. Additionally, some designs incorporate anti-loosening devices between chain links, such as spring washers or nylon lock nuts, to further enhance connection stability. For heavy-duty trailer chains, double-layer chain plates or cross-bracing structures are used to distribute load and improve overall torsional stiffness.
Process control directly affects the precision and durability of the connection structure. Chain link forming requires hot forging or precision casting processes to ensure uniform material density and avoid defects such as porosity and cracks. For example, hot forging refines the grain structure within the chain plates, improving fatigue resistance; while precision casting is suitable for complex chain links, reducing subsequent machining errors. During assembly, strict control of assembly force is required, using torque wrenches or collaborative robots to ensure consistent torque at each connection point, preventing breakage or loosening due to excessive tightness or looseness. Furthermore, surface treatment processes such as cathodic electrophoresis or powder coating can enhance corrosion resistance and extend service life.
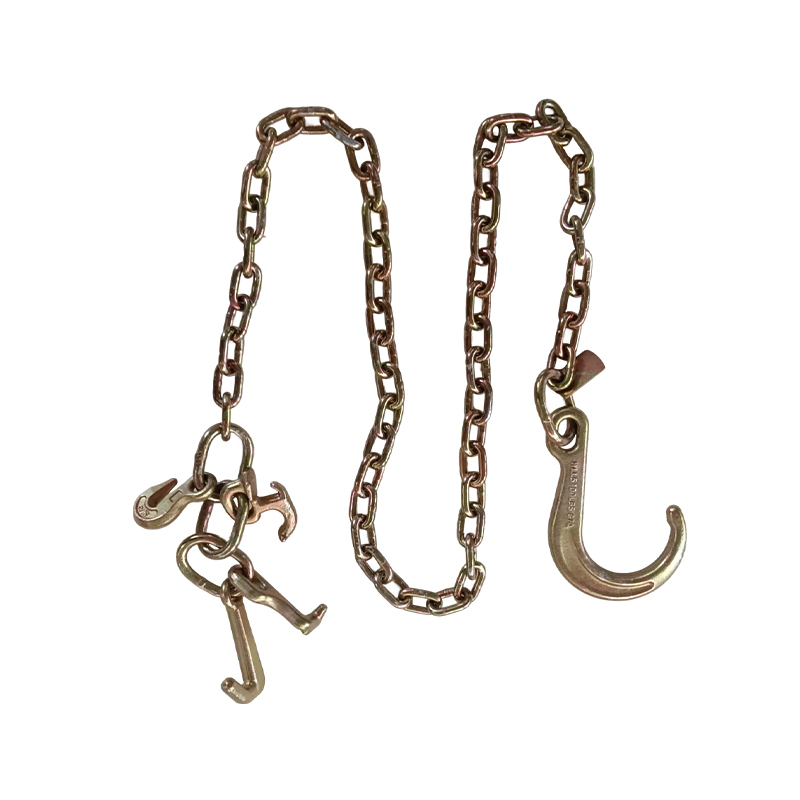
The design of auxiliary devices can further improve connection reliability. For example, trailer chains are often equipped with one-piece molded connectors at the ends, replacing traditional welding processes and avoiding stress concentration and brittle fracture at the weld seams. Metal bushings or reinforcing ribs may be embedded inside the connectors to improve tensile and shear strength. For long-distance traction scenarios, separators or cable fixing devices are also installed in the trailer chain to prevent internal cables and oil pipes from wearing down the connection points due to swaying. Some designs also add lubrication grooves or self-lubricating materials between chain links to reduce friction and wear, lowering the risk of connection failure.
Adaptive design under dynamic loads is an important guarantee for the reliability of the connection structure. Trailer chains are subjected to irregular torques and lateral forces during traction, especially under turning or bumpy road conditions. Therefore, some designs employ a low center of gravity structure to reduce the swaying amplitude of suspended parts; or optimize the shape of the chain links, such as using curved chain plates, to disperse stress concentration. Furthermore, the use of guide grooves or support frames can limit the movement trajectory of the trailer chain, preventing excessive bending or twisting and ensuring that the connection points are always under reasonable stress.
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential for the long-term reliability of the connection structure. Before use, check whether the chain links are deformed, cracked, or worn, whether the bolts are loose, and whether the connectors are intact. For plastic trailer chains, pay attention to signs of aging and brittleness; for steel trailer chains, check whether the anti-corrosion coating has peeled off. During use, avoid overloading, rapid acceleration, or sudden braking to reduce the impact of impact loads on the connection structure. For long-term storage, the trailer chain should be placed in a dry and ventilated environment to prevent rust or plastic aging caused by moisture.